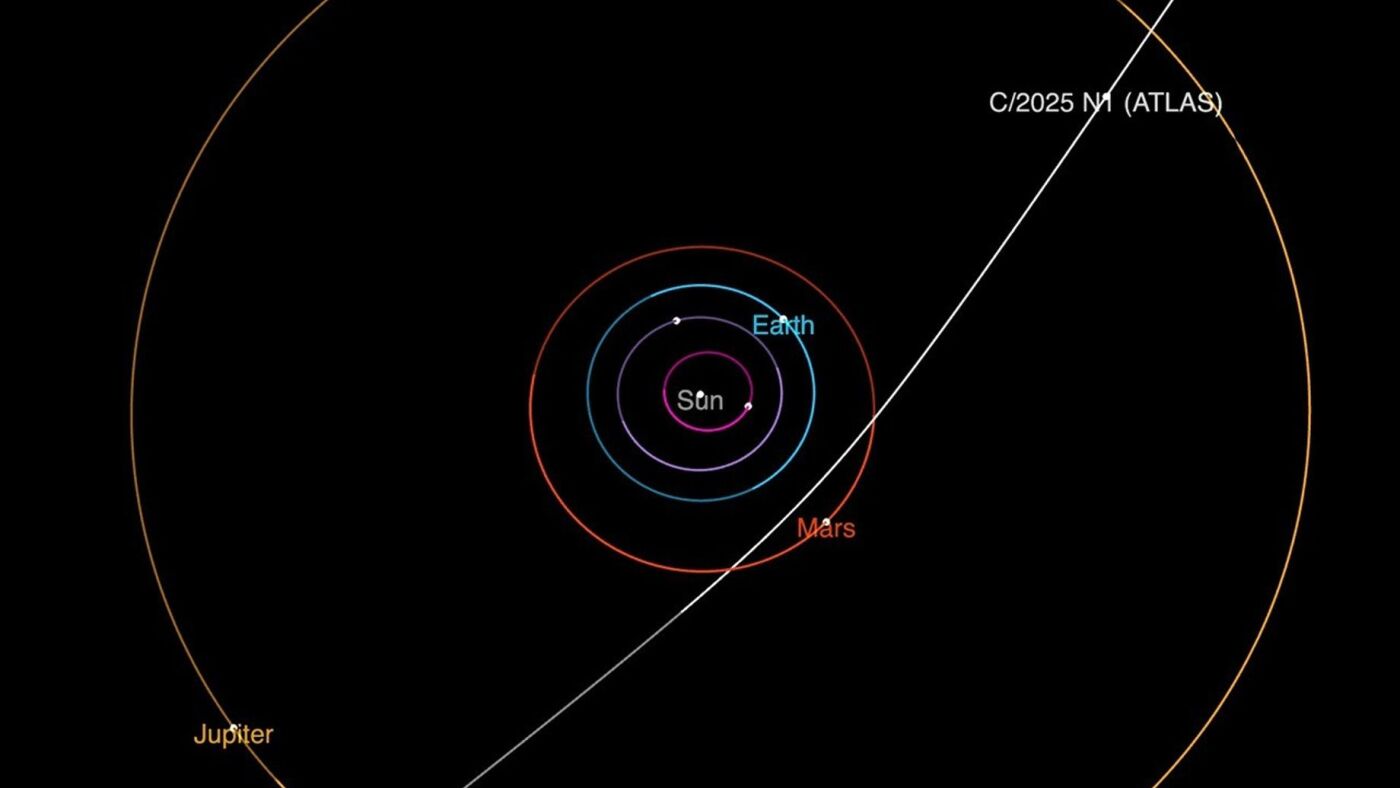
The vast expanse of space, once thought to be an impenetrable barrier, is proving to be more interconnected than we ever imagined. Our solar system, nestled within the Milky Way galaxy, occasionally receives visitors from afar—interstellar objects that have journeyed from distant star systems. Recently, NASA announced the discovery of a new interstellar comet, officially named 3I/ATLAS, marking only the third such object ever observed within our cosmic neighborhood. This celestial wanderer presents a unique opportunity for astronomers to study the composition and conditions of other star systems, offering a glimpse into the diversity of planetary formation beyond our own.
A Distant Discovery: Unveiling 3I/ATLAS
The discovery of 3I/ATLAS was made by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) survey telescope in Rio Hurtado, Chile. Funded by NASA, ATLAS is designed to detect near-Earth objects that could pose a potential threat to our planet. However, its wide field of view and sensitive detectors also make it capable of spotting more distant and unusual objects, such as interstellar comets.
The comet was first observed on July 1, 2024, and its trajectory quickly revealed its interstellar origin. Unlike comets that are gravitationally bound to our Sun, 3I/ATLAS is traveling on a hyperbolic orbit, meaning it will pass through the solar system only once before continuing its journey back into interstellar space. Its point of origin lies in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius, suggesting a long and arduous journey across the galaxy.
The Significance of Interstellar Visitors
The detection of interstellar objects like 3I/ATLAS is a relatively new phenomenon in astronomy. Before 2017, scientists had long theorized about their existence, but no concrete evidence had been found. The discovery of ‘Oumuamua in 2017, the first confirmed interstellar object, revolutionized our understanding of the frequency and nature of these cosmic wanderers.
Interstellar objects provide invaluable insights into the formation and evolution of planetary systems beyond our own. By studying their composition, size, shape, and trajectory, astronomers can learn about the building blocks of planets, the prevalence of comets and asteroids in other star systems, and the processes that shape their orbits.
Each interstellar object is a unique snapshot of its home system. They carry with them the chemical signatures and physical properties of their birthplace, offering a rare opportunity to directly sample material from another star system. Analyzing this material can reveal information about the types of stars, the age of the system, and the presence of water or other key ingredients for life.
3I/ATLAS: What We Know So Far
While observations of 3I/ATLAS are still ongoing, astronomers have already gleaned some important information about its characteristics. The comet is currently located approximately 420 million miles (670 million kilometers) from Earth. As it approaches the Sun, it is expected to reach its closest point in October, offering the best opportunity for detailed observations.
One of the key questions about 3I/ATLAS is its size. Determining the size of a comet is challenging, as it depends on factors like its distance, reflectivity, and the amount of dust and gas it is emitting. Early estimates suggest that 3I/ATLAS is relatively small, possibly only a few kilometers in diameter. However, further observations are needed to refine these estimates.
The composition of 3I/ATLAS is another area of intense interest. By analyzing the light reflected from the comet, astronomers can identify the chemical elements and molecules present in its coma (the cloud of gas and dust surrounding the nucleus) and tail. These observations can reveal whether 3I/ATLAS is similar in composition to comets in our solar system or if it has a more exotic makeup.
Challenges and Opportunities
Studying interstellar objects presents a unique set of challenges. Their transient nature and faintness make them difficult to detect and observe. Once an interstellar object is discovered, astronomers must act quickly to gather as much data as possible before it disappears back into interstellar space.
Despite these challenges, the potential rewards are immense. Interstellar objects offer a direct window into the diversity of planetary systems and the processes that shape them. By combining observations from ground-based telescopes, space-based observatories, and theoretical models, astronomers can piece together a more complete picture of the universe and our place within it.
The discovery of 3I/ATLAS has spurred a flurry of activity within the astronomical community. Telescopes around the world are being trained on the comet, and researchers are working tirelessly to analyze the data and extract meaningful insights. As 3I/ATLAS continues its journey through our solar system, it is sure to reveal more secrets about its origins and the nature of interstellar space.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Interstellar Object Research
The discovery of ‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov, the second interstellar comet discovered in 2019, has paved the way for future research in this exciting field. New telescopes and observing strategies are being developed to increase the chances of detecting more interstellar objects.
One promising avenue of research is the use of space-based telescopes. These observatories have the advantage of being above the Earth’s atmosphere, which can blur and distort images. Space-based telescopes can also observe at wavelengths of light that are blocked by the atmosphere, providing a more complete view of interstellar objects.
Another important area of development is the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies can help astronomers sift through vast amounts of data and identify potential interstellar objects that might otherwise be missed. They can also be used to analyze the complex data obtained from observations, extracting subtle patterns and relationships that can provide insights into the nature of these objects.
A Cosmic Invitation
The appearance of 3I/ATLAS is more than just a fleeting astronomical event; it’s a cosmic invitation. It beckons us to expand our understanding of the universe, to explore the diversity of planetary systems, and to consider the possibility of life beyond our own solar system. As this interstellar traveler journeys through our cosmic neighborhood, it carries with it the hopes and dreams of scientists and space enthusiasts around the world, offering a glimpse into the vast and mysterious realms beyond our reach.
The study of interstellar objects is still in its infancy, but it holds the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe. As we continue to discover and study these cosmic wanderers, we will undoubtedly uncover new secrets about the formation and evolution of planetary systems, the distribution of matter in the galaxy, and the potential for life beyond Earth. The journey of 3I/ATLAS is a reminder that we are all connected, part of a larger cosmic story that is still being written.